Tooth Infection: Symptoms, Types, and Warning Signs
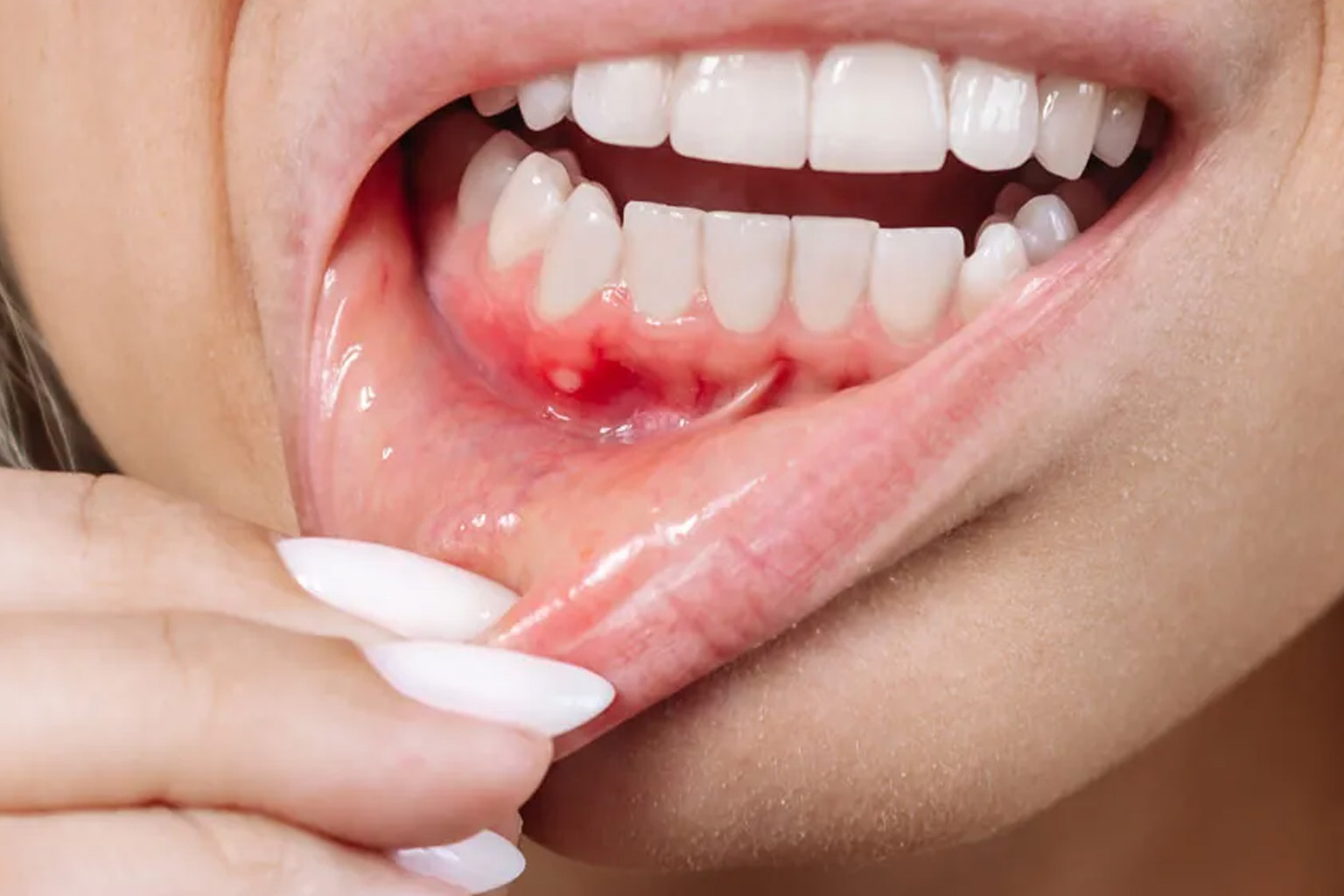
A tooth infection is one of the most common dental problems and can occur at any stage of life. Swollen, red gums accompanied by pain are often early signs of tooth infection. Recognizing the symptoms of a tooth infection in its early stages allows for timely treatment and helps avoid serious health complications.
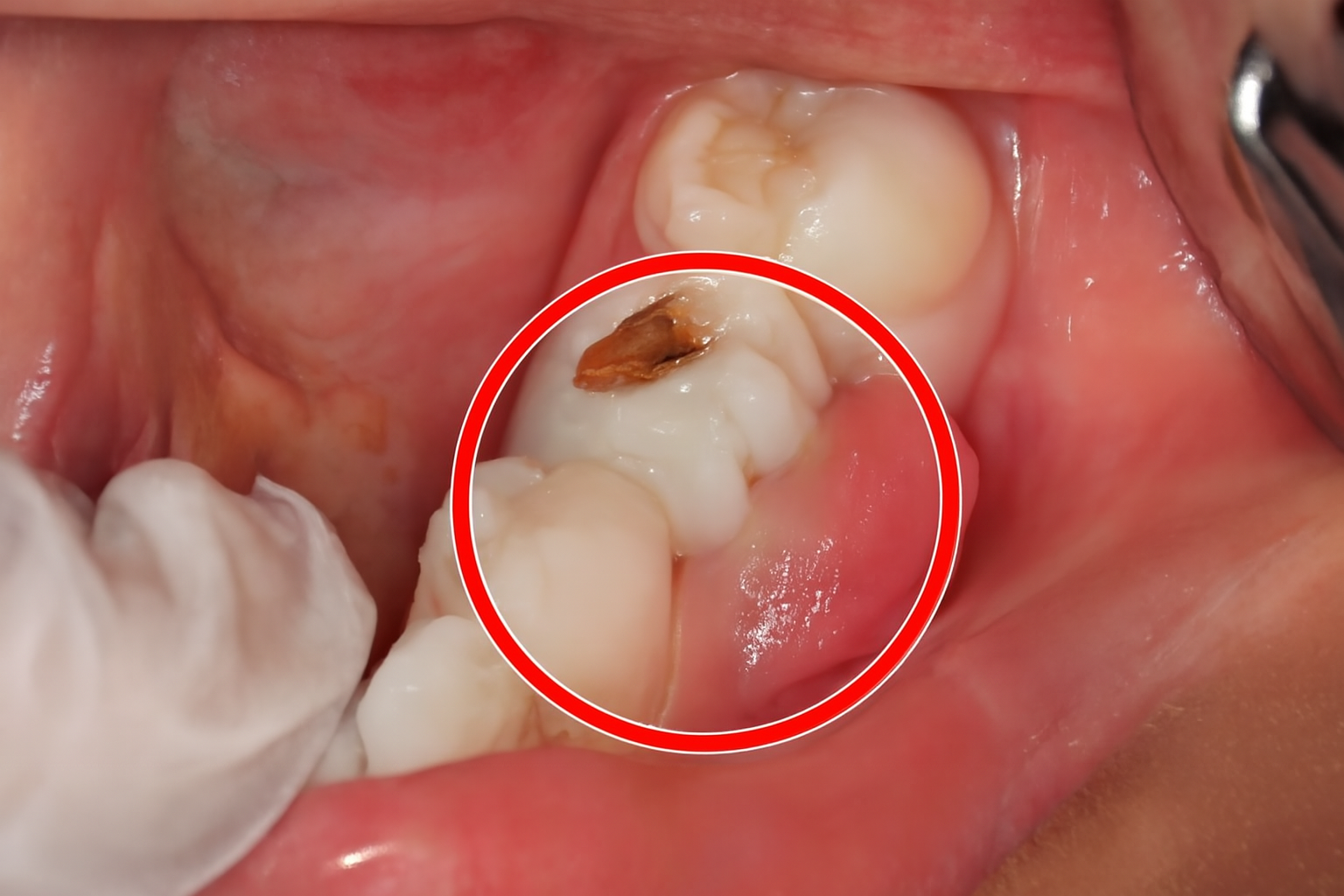
Infections can result from poor oral hygiene, untreated tooth decay, gum disease, or trauma. Without treatment, the infection can spread beyond the tooth and jaw, potentially leading to systemic conditions such as sepsis.
What Is a Tooth Infection?
A tooth infection occurs when bacteria enter the tooth’s inner structures—typically the pulp—through cavities, cracks, or gum pockets. Once inside, bacteria can cause inflammation, pain, and pus formation. Infections may remain localized, but if left untreated, they can spread to nearby tissues, lymph nodes, sinuses, or even enter the bloodstream.
Types of Tooth Infections and Dental Abscesses
There are several types of dental infections, depending on where they originate. Understanding these distinctions helps in proper diagnosis and treatment.
Gum Infection (Gingivitis / Gingival Abscess): Starts in the gum tissue and may affect adjacent teeth if untreated. It causes redness, swelling, and localized pain.
Periapical Abscess: Forms at the tip of a tooth’s root, often due to untreated decay or trauma. It affects the inner pulp and can spread to the surrounding bone.
Periodontal Abscess: Occurs in the supporting tissues of the tooth, such as the bone and periodontal ligament. It is commonly associated with advanced gum disease and is more frequent in adults.
Common Symptoms of a Tooth Infection
Tooth infections may present a wide range of symptoms. Some of the most common signs include:
-
Persistent, throbbing tooth pain that may radiate to the jaw, neck, or ear
-
Tooth discoloration (darkening compared to surrounding teeth)
-
Swelling in the face, gums, or jaw
-
Tender or swollen lymph nodes under the jaw or in the neck
-
Sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures
-
Pain while chewing or lying down
-
Fever, chills, and general fatigue
-
Bad breath or a foul taste in the mouth
-
Difficulty opening the mouth or swallowing
If you notice any of these symptoms, seek immediate dental care to prevent worsening of the infection.
Special Cases of Tooth Infections
1. Infection After Tooth Extraction
Tooth extractions, especially wisdom teeth, can sometimes lead to infection if proper aftercare is not followed. Signs of a post-extraction infection may include:
-
Severe pain in the socket or gums a few days after removal
-
Increasing swelling or redness around the jaw or face
-
Mild fever that gradually worsens
-
Pus or foul-smelling discharge from the extraction site
Prompt dental intervention is crucial to prevent further spread of infection.
2. Infection After Root Canal Treatment
Though rare, infections may occur after root canal procedures due to bacteria re-entering the tooth. Watch for:
-
Swelling of the jaw, face, or neck
-
Red or inflamed gums near the treated tooth
-
Tooth sensitivity to pressure or temperature
-
Persistent pain or throbbing
-
Loose tooth or tooth discoloration
These symptoms may signal the need for retreatment or further dental intervention.
3. Infection in a Filled Tooth
Improper fillings or underlying decay can lead to infection even after dental restoration. Key symptoms include:
-
Sharp or spontaneous toothache
-
Swelling and redness in the gums around the filled tooth
-
Presence of white pus or discharge
-
Discoloration of the filled tooth
-
Pain when chewing or applying pressure
If you notice any of these symptoms after a filling, visit your dentist to prevent complications.
Tooth Infection in Children
Tooth infections are not limited to adults. Children can also suffer from dental infections due to poor brushing habits, cavities, or untreated injuries. Common signs of tooth infection in children include:
-
Throbbing pain in the tooth or jaw
-
Swelling in the face or neck
-
Fever and chills
-
Refusal to eat or drink
-
Weight loss
-
Fatigue or irritability
Pediatric dental infections should always be taken seriously. Immediate diagnosis and treatment help preserve the child’s dental and overall health.
When to See a Dentist
Ignoring a tooth infection can lead to serious outcomes, including:
-
Tooth loss
-
Spread of infection to other parts of the body
-
Bone or tissue damage
-
Systemic infection (sepsis)
If you experience persistent pain, swelling, or any of the symptoms listed above, don’t wait. Contact your dentist immediately for evaluation and appropriate treatment.
Conclusion
Tooth infections can start subtly but escalate quickly. By recognizing the warning signs early and taking appropriate steps, you can prevent unnecessary pain and avoid life-threatening complications. Regular dental checkups, proper oral hygiene, and early intervention are key to maintaining a healthy smile.