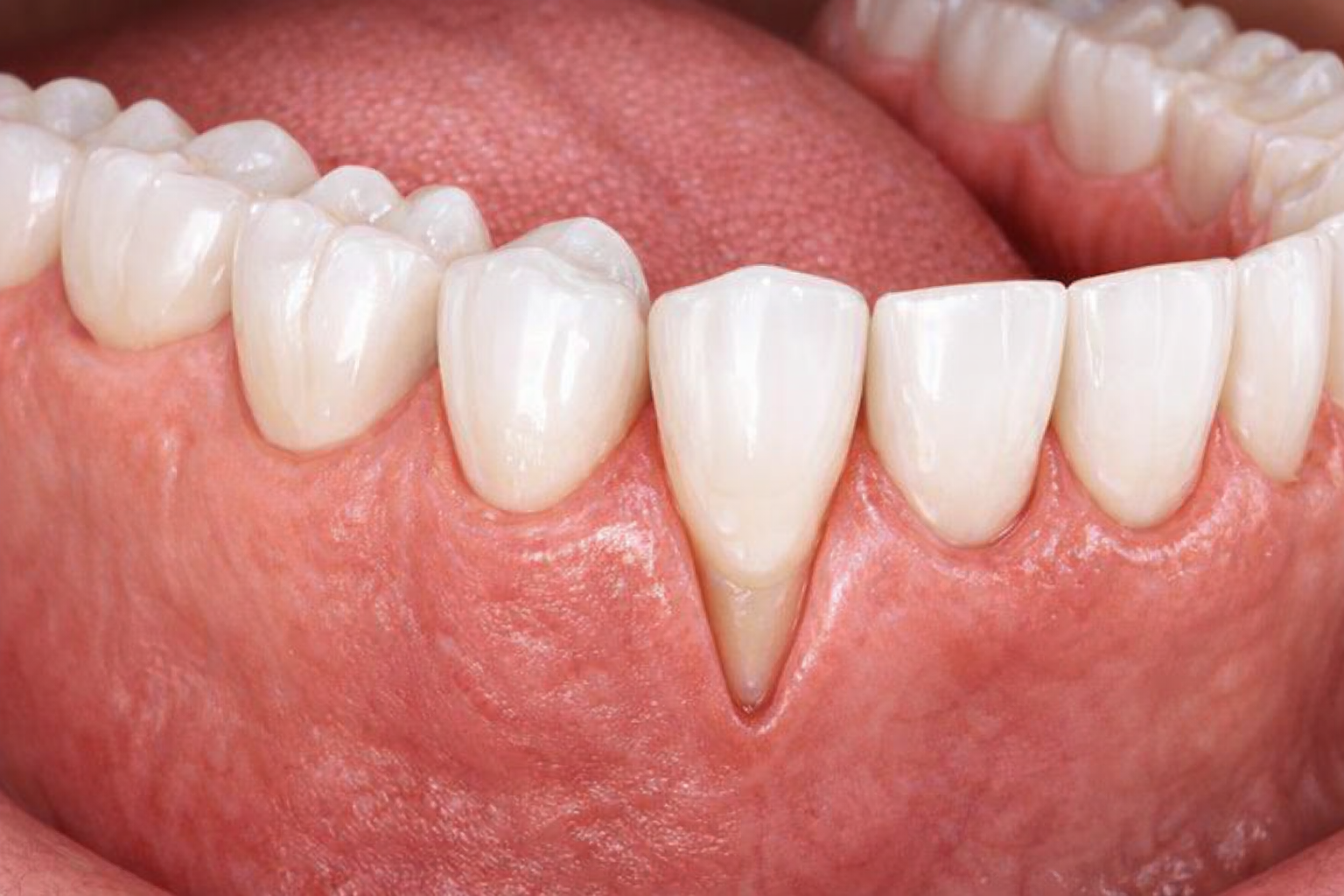
Gum recession is a typical dental issue that occurs when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth pulls back, exposing more of the tooth or its root.
When your gums pull back from your teeth, it’s called gum recession. This condition can lead to a variety of oral health problems, including tooth sensitivity, an increased risk of cavities, and even tooth loss if left untreated.
As a periodontist with expertise in periodontics and implant surgery, Dr. Nooshin Ghayoumi emphasizes the importance of understanding the causes of gum recession and the steps individuals can take to prevent or reverse it.
Who Does Gum Recession Affect?
Gum recession is not limited to any specific age group or demographic. It can affect people of all ages, although it tends to be more common as individuals age. The risk increases in people with poor oral hygiene habits, those who smoke, or who are very stressed.
Additionally, people with conditions such as periodontal disease or those who grind their teeth are more susceptible to gum recession.
While gum recession can happen to anyone, the extent of the recession and its impact on oral health can vary. Early signs may be subtle, but if left untreated, it can progress to a more severe condition. Therefore, identifying the causes early on and taking preventive measures can help avoid long term damage.
Common Causes of Gum Recession
-
Poor Oral Hygiene Habits
One of the leading causes of gum recession is inadequate brushing and flossing. When plaque and tartar build up on teeth, it can cause irritation and inflammation of the gums. Over time, this can lead to gum tissue loss. Consistent, effective oral care practices are essential for preventing gum recession.
-
Periodontal Disease
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is another major contributor. This bacterial infection attacks the gums and bone that support the teeth, causing the gums to pull away from the teeth and leading to gum recession. Periodontal disease often begins with gingivitis, a mild form of gum disease, and can advance to more severe stages if left untreated.
-
Genetics
Some individuals are genetically predisposed to thinner gums, which increases their risk of gum recession. If someone in your family has experienced a gum recession, you may be at a higher risk as well.
-
Aggressive Brushing
Using a hard-bristled toothbrush or brushing your teeth too aggressively can damage your gums. Over time, this can result in gum recession, particularly along the gumline. It’s essential to use a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle brushing techniques to protect your gums.
-
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menopause, or menstruation can make gums more sensitive and vulnerable to recession. This is particularly noticeable in women and may require more careful oral hygiene during these times.
-
Tobacco Use
Smoking or using other forms of tobacco can increase your risk of gum recession. Tobacco products cause inflammation of the gums and make it harder for the body to fight off infections, contributing to gum recession over time.
How to Reverse Gum Recession
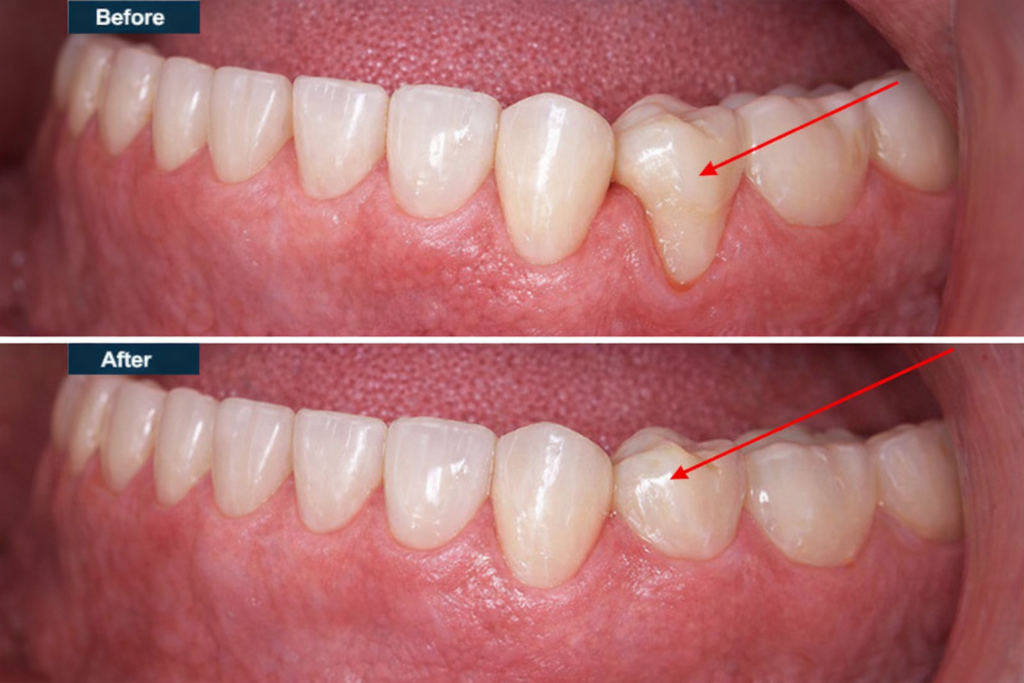
While gum recession is not always fully reversible, there are several methods to slow down its progression and even improve the appearance of your gums.
- Improve Your Oral Hygiene Routine
The first step in managing gum recession is improving your oral hygiene habits. Brush your teeth twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and floss daily. Regular dental checkups are also essential for catching early signs of gum disease and preventing further recession. - Use Desensitizing Toothpaste
For those experiencing tooth sensitivity due to gum recession, using toothpaste designed for sensitive teeth can provide relief. These toothpastes contain ingredients that help block pain signals from the tooth’s surface. - Surgical Procedures
In cases of severe gum recession, surgical procedures such as gum grafts may be necessary. A periodontist can perform a gum graft, which involves taking tissue from another area of your mouth or using synthetic material to cover the exposed tooth roots. - Scaling and Root Planing
If gum recession is caused by periodontal disease, a procedure called scaling and root planing may be recommended. This deep cleaning removes plaque and tartar buildup from below the gumline and smooths the tooth roots, which helps the gums reattach to the teeth. - Lifestyle Modifications
Quitting smoking, managing stress, and avoiding aggressive brushing can help prevent further gum recession. Your dentist or periodontist may also suggest using an antimicrobial mouthwash to help reduce bacteria in the mouth.
Conclusion
Gum recession can be a serious dental issue, but with proper care and treatment, its progression can be slowed, and in some cases, even reversed.
You can protect your gums and achieve a healthy smile through three methods, which include practicing proper dental care and getting professional dental assistance and changing your daily habits.
If you notice any signs of gum recession, it’s essential to consult with a dental professional as soon as possible to prevent further damage.
If you are concerned about gum recession or other periodontal issues, contact my office for a consultation at 949-502-8844. Protect your smile and oral health today!